HDPE Pipes
HDPE pipes are manufactured from raw material PE100 grade which is having maximum design stress, high temperature and chemical resistance.
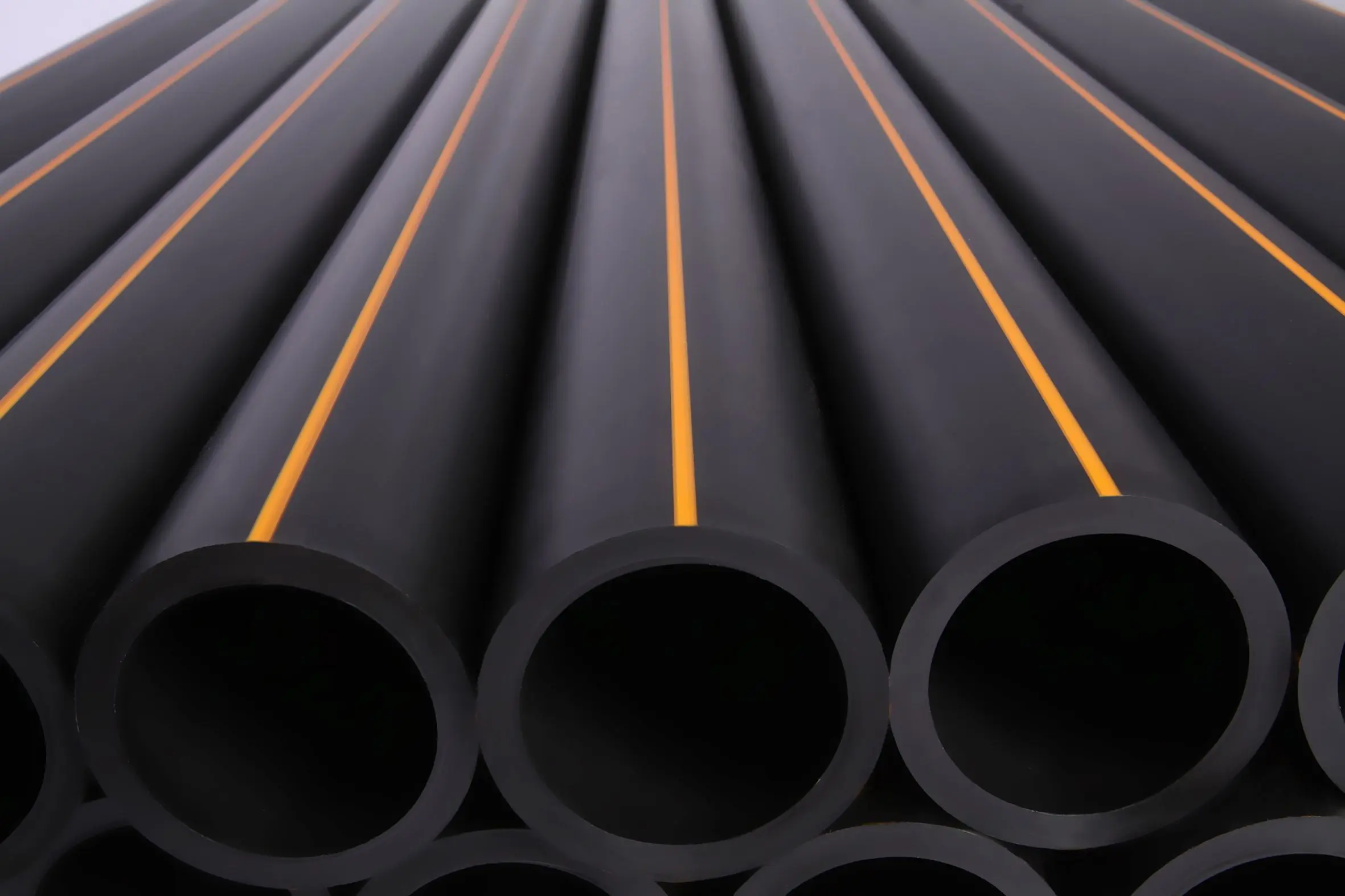
High Density Polyethylene Pipe (HDPE Pipe) is a hard, light, solid pipe with a smooth inner and outer surface. Transporting HDPE pipe requires little equipment and can be done in any field condition, such as on ice or in wet, marshy areas. HDPE pipes do not rust, making them indispensable to you. It's resistant to chemicals found in salt water and sanitary sewerage wastewater. Corrosive acids, bases, and salts are more resistant to corrosion than most pipe materials.
HDPE pipes are made by the polymerization of ethylene, a by-product of oil. Various additives (stabilizers, fillers, plasticizers, softeners, lubricants, colorants, flame retardants, blowing agents, crosslinking agents, ultraviolet degradable additives, etc.) are added to produce the final HDPE pipe and components. HDPE pipe lengths are made by heating the HDPE resin. It is then extruded through a die, which determines the diameter of the pipeline. Polyfab offers the best HDPE Pipes in Ethiopia, Ghana, Kenya, the United Arab Emirates, and internationally.
Download CataloguePressure HDPE Pipes
Potable water & Irrigation applications
- HDPE pipes can transport potable water, wastewater, slurries, chemicals, hazardous wastes, and compressed gases.
- HDPE Pipes have a long and illustrious history in the gas, oil, mining, and other industries.
- When compared to other pressure pipe materials used for urban gas distribution, they have the lowest repair frequency per mile per year.
- Polyethylene is a strong, extremely tough, and extremely durable material.
- High-density polyethylene pipe will meet all of your needs, whether you want long service, trouble-free installation, flexibility, chemical resistance, firefighting, or a variety of other features.
Download Catalogue

Fire Fighting applications
- HDPE pipes are non -corrosive, excellent chemical & wear resistance which may suite for many more fire fighting applications.
- PE material resistance to environmental stress cracking for long term performance.
- High impact resistance and stiffness to withstand internal pressure and external loads.
- Adhere to International Standards AWWA906
- Usage- Polyethylene (PE) pipes for Firefighting Application
- Size Range: 20mm to 630mm
- Pressure Rating: PN16, PN20
- Standard Dimensional Ratio: SDR11, SDR9
- Available in 6Meter, 12Meter & Rolls with red stripe
- FM approved
Download Catalogue

Gas applications
- HDPE pipes are non- toxic , Good toughness, effectively resistance to chemicals and long life span, these all properties are more suit this material for Gas applications.
- PE pipes are providing solutions for different kind of joints in gas network.
- Easy Installation
- Long service life
- Weatherability
- Quality Control
Download Catalogue

Polyfab is the largest HDPE distributor in Ethiopia, Kenya, Ghana, and the United Arab Emirates. We can serve your HDPE needs anywhere in Ethiopia, Kenya, Ghana, the UAE, and internationally due to our size and capabilities. There's a reason we're so proud to be an HDPE distributor: it's perfect for a variety of applications such as municipal, industrial, energy, geothermal, landfill, marine, and more.
Our pipe comes in Black color with blue, red, green, orange, yellow stripes. Further, we also produce pipes in full blue & orange colors as per the specific requirements.
This will be supplied in 6mtr, 12mtr& 100mtr Rolls.
Non-Pressure Pipes for Ducting
- HDPE duct are manufactured for mechanical protection of electrical and other cables.
- HDPE ducts are used for installation long-distance telephone networks, cable television transmissions, information transfer networks, etc.
- Due to high elongation and insulating properties this material is more suitable for ducting applications.
Download Catalogue

Drainage Systems for Soil & Waste Discharge
- Polyfab Plastic's HDPE drainage systems are the ideal solution for all types of drainage applications, including soil and waste management, above and below ground drainage, and chemical waste management. These pipes and fittings are made in accordance with the most recent European EN 1519 – 1 standard and can be assembled with butt-fusion, electro-fusion, flanges, or rubber ring joints.
- PE drainage systems have exceptional chemical resistance, a high temperature rating, flexibility, and low noise. Because of these characteristics, they are an excellent choice for residential and industrial buildings, laboratories, hospitals, and hotels.
- Polyfab Manufacture and supply all type of HDPE Drainage Plastic Piping System for above ground, underground and other chemical waste.
- Our HDPE division supply all types and sizes of fittings for drainage piping system with 32mm to 315mm sizes range. Higher sizes can provide segmented fittings as per requirement.
- Polyfab HDPE plastic piping system for soil and waste discharge is designed as per the International Manufacturing Standard of EN 1519.
Download Catalogue

Benefits of HDPE Pipes
High Density Polyethylene Pipe (HDPE Pipe) is a hard, light, solid pipe with a smooth inner and outer surface. Transporting HDPE pipe requires little equipment and can be done in any field condition, such as on ice or in wet, marshy areas. HDPE pipes do not rust, making them indispensable to you. It's resistant to chemicals found in salt water and sanitary sewerage wastewater. Corrosive acids, bases, and salts are more resistant to corrosion than most pipe materials. Polyfab offers the best HDPE Pipes in Ethiopia, Ghana, Kenya, the United Arab Emirates, and internationally.
HDPE pipes are easier to process and install, and they save money during construction. Other pipes tend to crack and break structurally. Polyfab HDPE pipe is designed to withstand cold weather impact during installation. Due to different kind of fusion welding techniques this HDPE pipes are more suitable for easy installation with more space constrain areas also. HDPE pipes can be mounted on the shore for extended periods of time and then fitted in place in marine applications.
FM Approval (USA)
Industrial and commercial companies around the world rely on products and services that are FM Approved and specification tested to protect their properties from loss. The FM APPROVED mark, which is backed by scientific research and testing, tells customers your product conforms to the highest standards. FM Approvals is an international leader in third-party certification and approval of commercial and industrial products.
POLYFAB manufactures FM approved PE Pipes and Fittings conforming to ISO 4427 standards with pressure rating SDR9 and SDR 11. Our range of FM approved things includes Elbows, Tee etc. as per EN 12201 standards. Under stringent quality control, our pipes and things are tested at each stage of production to comply with quality and standards.
Characteristics and Advantages of Polyfab HDPE Drainage System
Polyfab using highly qualified PE100 HDPE virgin material to manufacture pipe and fittings. Our PE Drainage pipes and fittings have excellent material properties of HDPE with homogenous welded joints provide greater installation flexibility with a wide range of connecting options. It is highly recommended to suit the internal building applications for commercial and industrial segment and underground drainage applications. It is highly recommended where the high impact or abrasion resistance is required to extend the life of the product as it is on continuous use.
What factors into the choice of HDPE pipe thickness?
The pressure of the water and the internal body pressure at which water will flow are two elements that affect the choice of HDPE pipe thickness. For example, when there is gravity water flow, a farmer will use the lowest gauge. Another grower that uses a water pump will use thicker plumbing that can withstand the pump's pressure. With increasing pipe thickness, water pump pressure rises.
Experiencing the weather outside While some growers prefer to install the pipes on the ground, others would rather have them buried underground. The former will employ heavier, more durable pipes that can withstand both mechanical damage and prolonged UV exposure. Since the pipes are resistant to mechanical deterioration and UV radiation damage from the sun, they can be used later.
The Pipe wall thickness is determined by a combination of the die size, speed of the screw, and the speed of the haul-off tractor. Usually, 3-5% carbon black is added to HDPE Pipe to make it UV resistant, which turns HDPE pipes into black in color. Other color variants are available but usually not used frequently. Colored or striped HDPE pipe is usually 90-95% black material, where a colored stripe is provided on 5% of the outside surface. Due to its low weight and high corrosion resistance, the HDPE pipe industry is growing tremendously.
HDPE Pipes Ethiopia
To create HDPE pipes that go above and beyond expectations, Polyfab employs the greatest materials, the best craftsmanship, and the most recent technology throughout the Ethiopian region. Our adaptable pipes can carry Potable Water, gases, chemicals, distribution lines, sewage, and drainage lines, among other things. Our pipes can also be used for garbage removal, irrigation, and sprinkler systems in addition to electrical and telecom ducting. With a size range of 20m to 400mm, it will be the best option for pipeline facilities throughout the Ethiopian region. Polyfab is supplying HDPE pressure pipes to most of Ethiopia’s world bank-funded government water supply projects.
HDPE Pipes Ghana
Polyfab HDPE division of Ghana offers all varieties of HDPE Pipes depending on the requirement. High-density polyethylene pipe is lightweight and affordable while offering durable, reliable performance. According to the Plastic Pipe Institute, it will last 50 to 100 years. The HDPE pipe market is booming in the waterworks sector.
HDPE Pipes Kenya
Polyfab is one of the major producers and suppliers of HDPE pipes across all of Kenya. Our business is dedicated to offering the best HDPE pipes on the market at affordable pricing. To ensure consistently high-quality output, we adhere to precisely controlled processing standards. We are dedicated to advancing plumbing, irrigation, and sewage technologies ceaselessly.